The internet has revolutionized how humans communicate and learn. With the advancement of technical infrastructure over time, video has rapidly become the preferred mode for learning and content sharing with a worldwide audience.
If you are a video content creator, you have undoubtedly wondered what technical aspects of video hosting you need to be familiar with to create the best possible viewing experience for your students and audience. There is so much talk of video quality and video resolutions, considerations on SD vs HD are likely made during video production as well as video publishing.
Researching the answer can unleash an avalanche of acronyms, abbreviations, and technical-sounding terms that bring more questions than answers. Luckily, we’re here to help you sort through this tangle of information, and zero-in on what metrics really matter when you’re deciding the best way to serve up your stellar content.
The Basics: Pixels and Video Resolutions
The terminology related to SD video and HD video can sound like a lot of jargon, but the reality is a lot simpler than it seems. Video streaming with SD video can cause you to suffer through grainy, pixelated footage, or on the other side of the equation ultra HD video can cause constant buffering and interrupted playback. So you’re already well aware of how video resolution can affect your viewing experience.
At the heart of it all is the humble pixel.
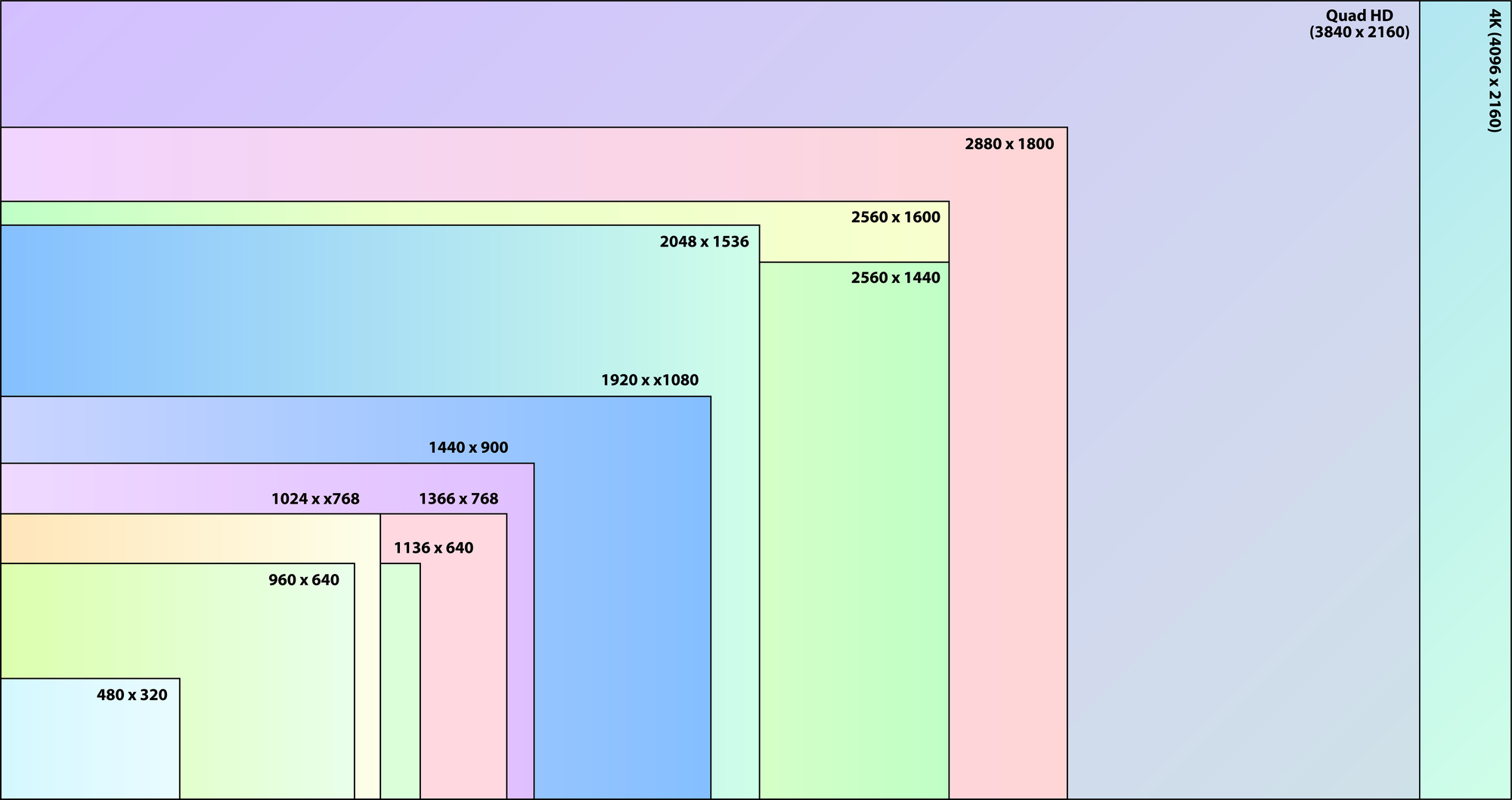
A pixel (or “picture element”) is just a tiny dot or square of illumination on a screen, capable of displaying any one of millions of colors. Whatever device you’re using (a computer attached to a monitor, a flat-screen tv, or a mobile device) translates data from photo and video files into directions that tell each individual pixel what to display and for how long. Put together, all of these pixels then form images that humans can see and understand. The more pixels a device screen has, the clearer the overall picture and the finer the level of detail that can be displayed.
This level of detail is known in the graphics world as resolution, and for tech it’s usually expressed in numeric form, such as ‘1920 x 1080’. This equation tells us that a screen has 1,920 vertical pixels and 1,080 horizontal pixels available for display, giving the screen an overall density of 2,073,600 pixels with which to show every detail of an image or video.
In an effort to be efficient and to the point: This metric is often short-handed within the industry as, in the example above, 1080p (using just the second or horizontal number in the equation) or 2.1 megapixels (the number of total pixels available).
Ultimately, the top resolution of a device represents the cap on what that device can display. A screen set to a resolution of, say, 480p, can’t display the full benefits of a 1080p video. The monitor you are using right now likely has a display resolution of 1920 x 1080.
Now that we know what we’re actually talking about when we refer to video resolution, we can talk about how all of this can affect video content you generate for your video course.
The DL on SD vs HD
If you’re offering video as part of your ecommerce site, elearning course, or blog then considerations for video resolutions need to play a part in your overall content strategy.
Standard definition (or SD video) is a term for video that is compatible with lower-resolution output, usually topping out at about 480p (or 858 x 480). The ‘p’ stands for progressive scanning. That means it updates full frame images faster than traditionally interlaced content.
While this level of video resolution was long an industry standard, rapid advances in screen technologies, as well as greater bandwidth accommodations for users, have meant that SD video has slowly been losing favor over the years.
High-definition (HD) has become the new de-facto standard. Videos in 720p, typically known as “standard HD video” or just “HD”, are very popular on the web. These videos come in at 1280 X 720. Offering greater picture clarity and sharpness, HD video has become the primary choice for content creators looking to create professional, high-quality output that will wow audiences with immersive imagery and pristine graphics.
And then you have 1080p video, known as “full HD video”, coming in at 1920 X 1080. When people typically say “HD” 1080p videos come to mind, but 720p videos are also technically HD.
SD vs HD Video Considerations for Video Hosting
Customers and video creators often ask 2 very popular questions when it comes to video hosting. The first being about video length: “what are video length best practices?” or “is my video too short or too long?“.
And the second being “should I host my videos in 720p or 1080p?“.
Clearly when it comes to hosting video today, HD is the way to go. Unless the absolute vast majority of your users are using mobile devices in areas of the world that have very poor mobile service, then you would rarely offer SD only.
At Spotlightr, we recommend 720p for most web, and especially eLearning, use-cases. At the size most web videos are served, the difference between 720p and 1080p is not very noticeable. It saves you on storage costs, bandwidth costs, and will stream better across most internet speeds.
Of course if your content really depends on the highest of quality (for example photography lessons), or you know your audience will always watch in full screen, then 1080p might be the better choice for you.
Video hosting companies, like us, also create multiple versions of your video in different video resolutions. So if you do prefer to serve 1080 videos, you can upload that and 720 and 360 versions will also be created. This way your users can switch resolutions if their internet speeds are slower.
There are some resolution levels above HD, specifically Ultra-HD (which Spotlightr also supports). Commonly known as 4k video, it refers to the horizontal resolution which is around 4000 pixels (the ‘k’ stands for kilo, or 1000). These display at 3840 x 2160 pixels (nearly 8.3 megapixels).
While popular with content creators working in video game streaming—where graphics are an important component of gameplay—4k has been slower to roll out to broader audiences, though many see it as the inevitable future of video.
Standard-definition and High-defintion: Pros and Cons
Pro: Quality (of course)
The selling points of HD resolution video are hard to dispute: with high-definition, you get color-rich, crystal-clear video content that brings a polished and professional look straight to your target audience. High-definition videos also port seamlessly from one screen to another, meaning that they can look great on television, monitors, tablets, or mobile devices. This dependable flexibility is helpful for creators looking for wide accessibility that doesn’t require a huge effort in production.
Con: Dependent on internet speeds
For the majority of the world, when talking about Full HD video, also known as 1080, internet speeds are plenty fast. But this is still a consideration worth mentioning if you are looking to stream at higher resolutions like 4K or if your audience is located in parts of the world that aren’t caught up yet.
High-definition video depends upon faster internet speeds for the best possible picture quality. While bogged-down bandwidth is just an occasional occurrence in many places, slower internet speeds can be more common than you think throughout the world (according to surveys of global broadband speed).
While the mean download speed in the United States is 92.42 Mbps (megabytes per second), many countries in Africa have mean download speeds south of 5 Mbps. Even China has a mean download speed of just 2.06 Mbps–thanks to extensive rural districts.
As mentioned earlier Spotlightr does create multiple video resolutions, meaning multiple versions of your video are generated. So keep that in mind when uploading your content. When uploading a video in 1080, we will produce a version that is 720 and 360 so that users with slow internet speeds can lower the resolution of the video to prevent the video from buffering.
On mobile the video format will often be standard definition video. SD video creates smaller files that are faster to download, and requires less bandwidth to stream. Popular for users with older tech equipment (or slower broadband access), standard definition is often the preferred video resolution. It presents the best trade-off between visual quality and ease of use.
Con: More bandwidth used
More on this below, but just something to keep in mind. Higher quality videos consume more bandwidth. This may or may not be a concern for you when hosting your videos with a video hosting company.
How Do Pixels Affect Bandwidth Limits for Video Hosting?
We have already established that the higher the pixel density, the higher the quality. So it’s logical to assume that higher pixel density and higher quality brings with it higher data usage.
And let’s take that a step further and say that the more data you use when people watch your videos, the more money you pay to host your video content. This brings us to bandwidth.
You often see the word bandwidth thrown around when looking for video hosting or dealing with your video hosting account. Bandwidth is simply the data that is used when people watch your videos. The more minutes that are watched, the more bandwidth is used.
So one thing to consider when exporting your video content and getting it ready for your video host and audience is how the quality of your video will affect costs. The formula is pretty simple:
Higher quality videos = More bandwidth used = Higher costs
So let’s explore that a bit…
Video Resolutions & Bandwidth
The differences in bandwidth used when videos are watched at different quality levels is quite drastic. Let’s take a real example of this to show you how this might affect your bandwidth usage with your video hosting company.
Here is an original full HD video downloaded from our Storyblocks account. It’s in 1080p with a bitrate of 25. The file that was uploaded was 185 MB. As you can see from the video quality, it’s definitely high definition.
Then we took that original fize and ran it through Handbrake to create an HD video. We set the resolution to 720 and kept the original bitrate of 25. The resulting size of the video was 87 MB.
So because the video size is now less than half of the 1080 version, you will be using less than half of the bandwidth you’d use with 1080 videos. In real numbers if you are using 200 GB of bandwidth with 1080 videos, the exact same amount of video views with 720 videos will consume about 94 GB.
That means you will see significant cost savings as far as bandwidth is concerned. And video quality is still quite good when compared to the full HD resolution.
Finally let’s see how this same video looks when compressed and exported at 480p (720 x 480). This file size shrunk down to 58 MB. (It’s a long story but yes this can display at 16:9 aspect ratio)
Battle Royale SD vs HD: Which Video Resolution Reigns Supreme?
Well, certainly HD reigns supreme. But at this point, there are differences in HD to consider. Opting for certain resolution levels for your video output comes down to: a) knowing your audience, b) knowing how they prefer to consume your content, c) knowing the average specs of the devices and internet services they use, and d) knowing how your video quality will affect your bandwidth use.
While the crisp, clear quality of full HD video makes great sense for audiences in areas with high-speed internet connections consuming content with lots of detail, content aimed at broader or international audiences should consider whether the benefits of very high-quality video are offset by potential technical frustrations that could mar the viewing experience. Not to mention the additional storage and bandwidth consumption for your video hosting account.
All in all, at Spotlightr we recommend uploading video at “HD” 720 for most use-cases. There are too many benefits to 720 to ignore, especially considering most viewers consume videos on video players with sizes making it difficult to really tell the difference between 720 and 1080.
However, if you suspect your audience will watch in full screen, or there are details in the video necesssary to communicate your message that require higher resolution, then go ahead and upload at “Full HD” 1080.
Host & Stream Your HD eLearning Video Content
Spotlightr is the #1 choice for course creators and e-learning professionals. Sign up for a free trial, no credit card required, and discover the easiest & quickest way to get your video courses online. Integrates with everything you need and tracks all of your student viewing activity.

